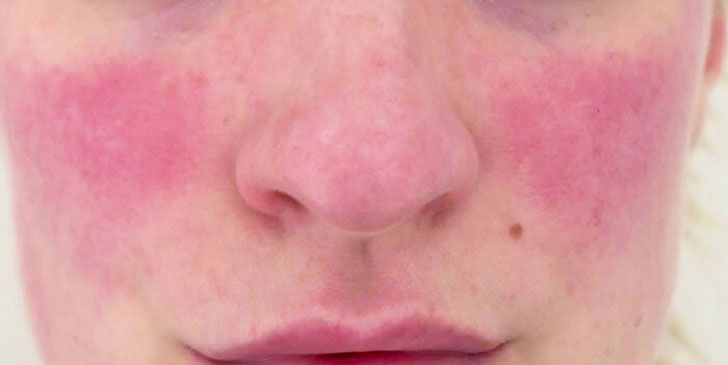
Rosacea is a chronic relapsing disease of the facial skin. It is characterised by recurrent episodes of facial flushing with persistent erythema, telangiectasia, papules and pustules. Ocular rosacea is usually bilateral and causes a foreign-body sensation.
• The prevalence of rosacea is highest among Indo-Eurasians. In Europe, there is an increasing prevalence from South to North: in Germany prevalence is 2.2%, in Sweden 10% and in Estonia 22%
• Rosacea is primarily a condition of the white population, is three times more common in women than in men and has a peak age of onset between 30 and 60 years.
• For a diagnosis to be confirmed the erythema should have been present for at least three months.